
Related articles
Read more

Egg quality plays a crucial role in female fertility and the ability to conceive naturally. While age and genetics are important factors, growing research shows that nutrition and lifestyle choices can significantly influence egg health. Eating the right foods can Improve Egg Quality, support hormone balance, protect eggs from oxidative stress, and provide the nutrients needed for healthy ovulation and embryo development.
In this article, we explore the best foods to boost egg quality and help you get pregnant faster, backed by scientific evidence. Whether you are trying to conceive naturally or preparing for fertility treatments, understanding how to improve ovum quality through diet can empower you to make informed choices that support your reproductive health and overall well-being.

Understanding the signs of bad egg quality is the first step in taking control of your fertility. While many women look for physical symptoms of bad egg quality, these indicators can often be subtle or silent. The most frequent clinical signs include irregular menstrual cycles, difficulty staying pregnant, or low ovarian reserve markers in blood tests. By recognizing these signs early, you can implement dietary changes to protect your remaining eggs and improve your chances of conception.

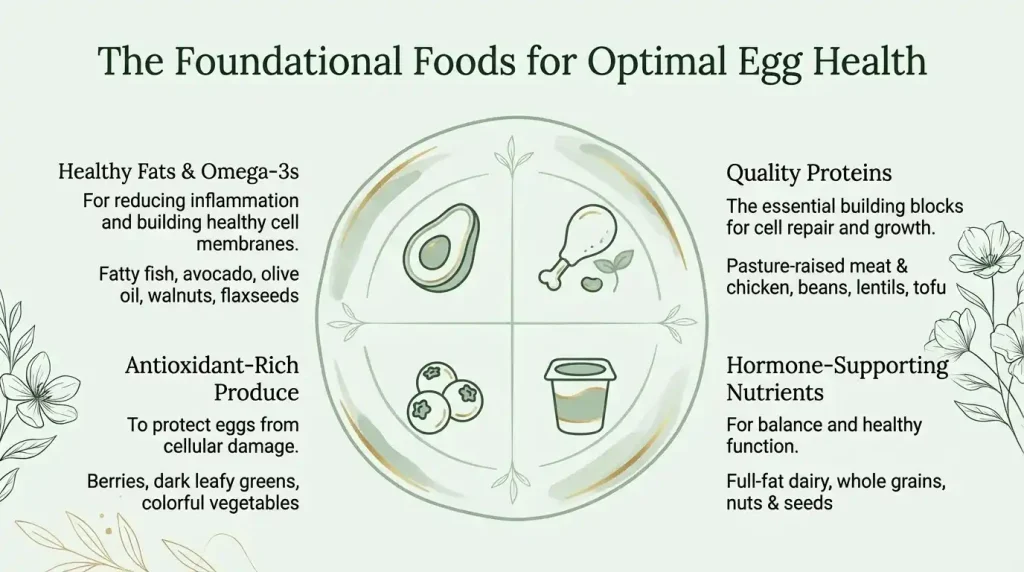
A healthy diet plays a key role in supporting overall reproductive health. The right combination of nutrients can help improve egg quality, protect eggs from oxidative stress, support hormone balance, and provide the building blocks needed for normal egg development. The following dietary components are commonly associated with better ovarian and egg health.
Full-fat dairy products such as whole milk, yogurt, and cheese provide essential fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamins A, D, E, and K, which play a role in hormone production and egg development. Unlike low-fat versions, full-fat dairy helps support stable blood sugar levels and satiety, which is important for hormonal balance. Choosing high-quality, minimally processed dairy can contribute to overall reproductive health without unnecessary additives.
Unsaturated fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids, are crucial for healthy egg cell membranes and normal ovulation. These fats help reduce inflammation and support proper hormone signaling. Foods such as fatty fish, olive oil, avocado, and flaxseeds are excellent sources. A diet rich in omega-3s has been associated with improved egg quality and better overall fertility outcomes.
Pasture-raised meat and chicken tend to contain higher levels of nutrients like zinc, iron, and vitamin B12, which are important for egg development and ovarian function. These proteins also provide essential amino acids needed for cell repair and growth. Choosing pasture-raised options can reduce exposure to hormones and antibiotics commonly found in conventionally raised meats.
Organic fruits and vegetables are valuable sources of vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds that support reproductive health. Choosing organic options may reduce exposure to pesticides, which can negatively affect hormone balance. A varied intake of colorful produce ensures a broad range of nutrients that help protect eggs from environmental and oxidative stress.
Nuts and seeds provide healthy fats, protein, selenium, and vitamin E, all of which support egg health and protect reproductive cells from damage. Almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds are especially beneficial. Regular consumption in moderate amounts can help maintain hormonal balance and support ovarian function.
Certain vitamins and supplements may help fill nutritional gaps that diet alone cannot cover. Key nutrients such as folate, vitamin D, and B-complex vitamins are involved in egg maturation and hormone regulation. Supplements should be used thoughtfully and ideally under medical guidance to avoid excessive intake or nutrient imbalances.
Iron plays an important role in oxygen delivery to reproductive tissues and supports regular ovulation. Women with low iron levels may benefit from supplementation, particularly if dietary intake is insufficient. Iron supplements should only be taken when needed, as excessive iron can have negative health effects.

Royal jelly is a natural substance rich in amino acids, vitamins, and antioxidants. It has traditionally been associated with reproductive health and may help support hormonal balance. While scientific evidence is still limited, some studies suggest it may contribute to improved egg quality due to its nutrient profile.
Antioxidant-rich foods help protect eggs from oxidative stress, which can damage cells and affect fertility. Berries, dark leafy greens, green tea, and colorful vegetables are excellent sources. Including a wide range of antioxidants in the diet supports cellular health and may slow age-related egg damage.
Fiber-rich foods help regulate blood sugar and support healthy estrogen metabolism, both of which are important for egg health. Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits promote digestive health and reduce inflammation. Adequate fiber intake contributes to a more balanced hormonal environment and overall reproductive wellness.

In addition to a balanced, nutrient-dense diet, certain foods may offer extra support for egg health by improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and supporting hormonal balance. These foods are not miracle solutions, but when consumed regularly as part of a healthy lifestyle, they can contribute to better ovarian function and overall reproductive well-being.
When trying to conceive, certain foods and drinks can negatively affect egg quality, hormone balance, and fertility. Limiting or avoiding these items can help create a healthier environment for ovulation and conception.
Artificial sweeteners may disrupt gut health and hormonal balance, potentially affecting reproductive function. Choosing natural sweeteners in moderation is generally a safer option for fertility.
High caffeine intake and alcohol can interfere with hormone regulation and ovulation. Reducing coffee, energy drinks, and alcohol can improve the chances of conception and support overall reproductive health.
Some studies suggest that certain genetically modified (GM) foods may impact gut and hormonal health. While evidence is limited, opting for non-GM or organic alternatives can reduce exposure to potential risks.
Diets high in unhealthy fats, especially trans fats and heavily processed foods, can promote inflammation and insulin resistance, which may negatively affect egg quality. Choosing healthy fats in moderation is recommended to support fertility.

It is natural for fertility to change once you reach your mid-30s. Focusing on improving egg quality after 35 is a great way to give yourself a better chance of getting pregnant. By the time you reach 40, healthy food and lifestyle choices become even more important to protect your eggs and support your body.
The main goal for women in their late 30s and early 40s is to protect their cells from damage and keep their hormones balanced. Eating foods full of antioxidants—like berries, spinach, and colorful veggies—is one of the best natural ways to protect your eggs as you get older.
Also, adding healthy fats like Omega-3s (from fish and walnuts) helps keep your eggs strong and healthy. Getting enough protein from healthy sources is also important for cell repair. Other things, like managing stress and getting good sleep, are just as important for improving egg quality at 40. If you start these healthy habits early—ideally around age 35—you can prepare your body and increase your chances of having a healthy pregnancy.

For women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), the journey to improve ovum quality often involves managing insulin resistance and systemic inflammation. High insulin levels can trigger the ovaries to produce excess androgens (male hormones), which can hinder egg maturation and lower overall quality.
By focusing on these PCOS-specific dietary adjustments, you can create a more favorable environment for your eggs, even when dealing with hormonal imbalances.

It takes about 90 days for an egg to fully grow and be ready for release. However, you can still make the environment around your eggs much better in a shorter time. Depending on how much time you have, you can try these simple plans:

If you are in a hurry—maybe you have a doctor’s appointment or a treatment coming up—this 10-day plan can help give your body a quick boost.

If you want to improve egg quality in 30 days, starting a 30-day fertility diet is a perfect way to help your body find a healthy rhythm. A month gives your cells time to repair and helps your hormones stay balanced.

In this section, we will answer the most common questions about foods, nutrients, and dietary habits that can help improve female egg quality.
Learning how to Improve Egg Quality is all about a balanced diet and healthy habits. By eating the right foods for egg quality, like leafy greens and healthy fats, you can support your ovaries and protect your eggs from damage. Whether you are starting a 30-day fertility diet or making long-term changes, these steps will help Improve Egg Quality and increase your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
