
Related articles
Read more

Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone that plays a vital role in early pregnancy. In some cases, doctors prescribe HCG injections to support pregnancy, especially for women facing fertility challenges or a history of pregnancy complications. These injections are commonly used in fertility treatments and during early pregnancy to help the body maintain the hormonal balance needed for successful implantation and growth of the embryo.
In this article, we will explain what HCG injections are, why they are used during pregnancy, how they work in the body, and who may benefit from them. We will also discuss their potential benefits, risks, and important considerations, so you can better understand how HCG injections may help support a healthy pregnancy.

Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone that is produced very early in pregnancy. It is made by specialized cells called trophoblast cells, which later develop into the placenta. These cells begin releasing HCG shortly after a fertilized egg implants into the lining of the uterus, usually about 6–10 days after ovulation.

Once implantation occurs, HCG enters the mother’s bloodstream and urine. This hormone plays a crucial role in supporting early pregnancy by signaling the body that pregnancy has begun. One of its main functions is to stimulate the ovaries to continue producing progesterone, a hormone essential for maintaining the uterine lining and preventing menstruation.
As pregnancy progresses, HCG levels rise rapidly during the first trimester, often doubling every 48–72 hours in early weeks. Around 8–11 weeks of pregnancy, HCG levels typically peak. After this point, the placenta takes over progesterone production, and HCG levels gradually decline and stabilize for the remainder of the pregnancy.
Because HCG appears in the blood and urine soon after implantation, it is the hormone detected by home pregnancy tests and blood pregnancy tests, making it a key marker for confirming pregnancy.

As pregnancy progresses, HCG levels rise rapidly during the first trimester, often doubling every 48–72 hours in early weeks. Around 8–11 weeks of pregnancy, HCG levels typically peak. After this point, the placenta takes over progesterone production, and HCG levels gradually decline and stabilize for the remainder of the pregnancy.
Because HCG appears in the blood and urine soon after implantation, it is the hormone detected by home pregnancy tests and blood pregnancy tests, making it a key marker for confirming pregnancy.

An HCG ampoule injection is mainly used in fertility treatment rather than in a normal, naturally occurring pregnancy. Doctors prescribe this injection to help the body ovulate or to support the early hormonal phase needed for conception and implantation.
Most commonly, an HCG injection is given to trigger ovulation. It is administered when ovarian follicles have reached the right size, usually confirmed by ultrasound and blood tests. After the injection, ovulation typically occurs within 24 to 36 hours, allowing doctors to accurately time intercourse, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or egg retrieval in IVF cycles.
In some fertility protocols, HCG may also be injected after ovulation or embryo transfer to support the luteal phase. The hormone stimulates progesterone production, which helps maintain the uterine lining and supports early pregnancy until the placenta can produce hormones on its own.
hCG ampoules are not routinely injected during a confirmed natural pregnancy, as the placenta naturally produces adequate amounts of hCG once implantation has occurred. Using hCG injections without medical supervision is not recommended and may lead to side effects such as hormonal imbalance or ovarian hyperstimulation.
Overall, the timing and use of hCG injections depend entirely on a doctor’s assessment and are typically limited to specific stages of fertility treatment, not routine pregnancy care.
HCG injection is commonly used in fertility treatments to trigger ovulation at the right time. The timing of the injection is crucial to ensure that the eggs are released when they are fully mature, increasing the chances of conception. Doctors usually recommend the injection after monitoring the growth of ovarian follicles through ultrasound and hormone tests. Once the follicles reach the optimal size, typically around 18–24 mm, the HCG injection is given.
Ovulation usually occurs 24 to 36 hours after the HCG injection, which allows doctors to accurately schedule intercourse, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or egg retrieval in IVF cycles. Taking the injection too early or too late can affect ovulation timing and reduce the chances of successful fertilization.
It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully, as the dosage and timing of HCG depend on individual fertility conditions. Self-administering HCG without medical supervision is not recommended, as it may cause side effects like ovarian hyperstimulation, abdominal pain, or hormonal imbalance.
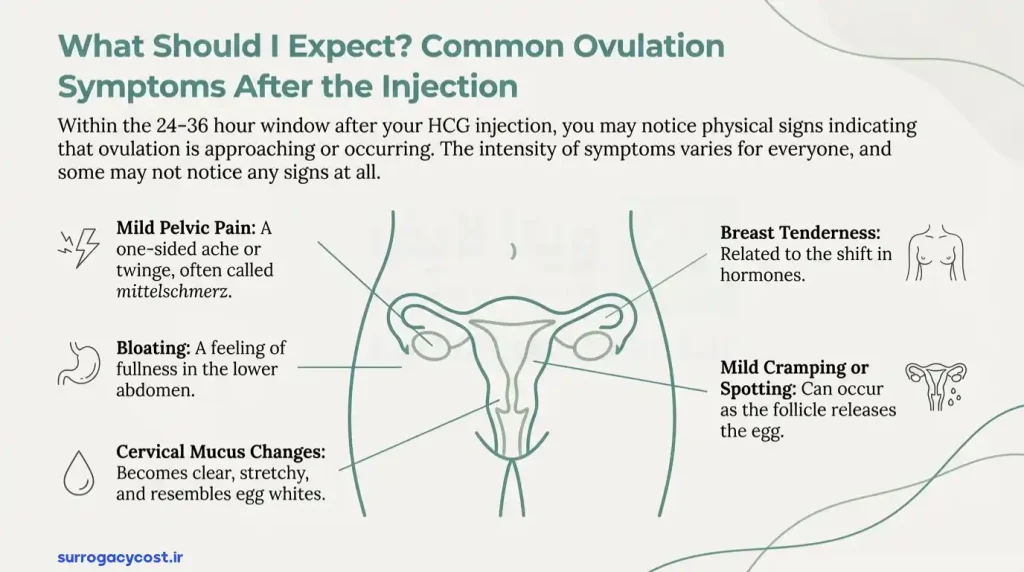
After an HCG injection, ovulation usually occurs within 24 to 36 hours, and many women notice certain physical and emotional signs that indicate ovulation is approaching or happening. One common symptom is mild pelvic or lower abdominal pain, often called mittelschmerz, which can occur on one side depending on which ovary is releasing an egg. Some women may also experience bloating or a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen as the follicles release the egg.
Other ovulation symptoms after HCG injection can include increased cervical mucus, which becomes clear, stretchy, and similar to egg whites, making it easier for sperm to travel to the egg. Some women notice breast tenderness or mild cramping, which is related to hormonal changes triggered by ovulation. Mood changes, mild fatigue, or slight spotting can also occur in response to hormonal shifts.
It’s important to note that the intensity and type of symptoms vary from woman to woman, and some may not notice any signs at all. Monitoring these symptoms along with ultrasound and blood tests, as advised by a fertility specialist, helps confirm that ovulation has occurred successfully after HCG injection.
Sometimes, even after an HCG injection, ovulation may not occur as expected. This can happen due to immature or unresponsive ovarian follicles, hormonal imbalances, or underlying fertility conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In some cases, the timing of the injection or dosage may not have been optimal, preventing the follicles from releasing the egg.
Women who do not experience typical ovulation signs, such as mittelschmerz, cervical mucus changes, or mild cramping, may need ultrasound monitoring or blood tests to confirm whether ovulation has occurred. Fertility specialists may adjust treatment by giving a different HCG dose, combining it with other medications, or scheduling additional ovulation support.
It is important to follow medical guidance closely, as skipping monitoring or self-adjusting doses can reduce the chances of successful ovulation and conception.

After HCG injections and successful ovulation, early pregnancy signs can appear as the embryo implants in the uterus. One of the first noticeable signs is implantation bleeding or spotting, which may occur around 6–12 days after ovulation. Some women experience mild cramping similar to menstrual cramps during this period.
Hormonal changes triggered by HCG can also cause breast tenderness, swelling, or sensitivity, often accompanied by fatigue and a heightened sense of smell or taste. Nausea or mild morning sickness may begin in the first few weeks, although not every woman experiences it.
Other early indicators include frequent urination due to increased blood flow and HCG levels, as well as subtle mood changes or irritability caused by hormonal fluctuations. Tracking these signs along with a pregnancy test is the most reliable way to confirm pregnancy after HCG injections.

The dosage of HCG injections varies depending on the purpose of the treatment and the patient’s individual response. For ovulation induction, doctors typically prescribe a single injection ranging from 5,000 to 10,000 IU, timed to trigger the release of a mature egg. In some cases, a lower dose of 2,000 to 3,000 IU may be used for women with a high risk of ovarian hyperstimulation.
For assisted reproductive techniques like IVF, the dosage is often tailored based on ultrasound monitoring of follicle development and hormone levels. The goal is to ensure that ovulation occurs at the optimal time without overstimulating the ovaries.
It is essential that HCG injections are administered under medical supervision, as incorrect dosage can lead to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), hormonal imbalances, or failed ovulation. Fertility specialists adjust the dose based on age, ovarian reserve, and previous response to treatment to maximize the chances of successful conception.

HCG injections are typically given subcutaneously (under the skin) or intramuscularly (into the muscle), depending on the type of HCG prescribed and the doctor’s instructions. Subcutaneous injections are usually administered in the lower abdomen or thigh, while intramuscular injections are often given in the buttocks.
Before injection, it is important to wash your hands and clean the injection site with an alcohol swab to prevent infection. The HCG solution should be mixed or reconstituted exactly as directed if provided in powder form. Using a sterile syringe and needle, the injection is administered at a 45- to 90-degree angle depending on the method.
After injecting, it is recommended to avoid rubbing the area vigorously, though gentle pressure can help reduce minor bleeding or bruising. Proper disposal of needles and syringes is essential for safety. Following the doctor’s guidance ensures the injection is effective and minimizes the risk of side effects.

HCG injections are not suitable for everyone and should be avoided in certain medical conditions. Women with ovarian cysts, uncontrolled thyroid disorders, or hormone-sensitive cancers should not use HCG without careful medical supervision. Those with a history of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) are also at higher risk of complications from HCG injections.
HCG is generally not recommended for women who are already pregnant naturally, as additional injections are unnecessary and could cause hormonal imbalance. Individuals with allergies to HCG or its components should avoid it, as allergic reactions can occur.
Doctors may also advise caution in patients with severe liver, kidney, or heart problems, because HCG can affect fluid balance and hormonal regulation. A thorough medical evaluation is essential before starting HCG injections to ensure safety and effectiveness.

HCG injections can cause side effects, ranging from mild to serious. Common mild effects include injection site pain, redness, or swelling, headaches, fatigue, and mood changes. Some women may experience bloating, mild abdominal discomfort, or breast tenderness due to hormonal fluctuations.
More serious risks include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), especially in women undergoing fertility treatments. OHSS can cause severe abdominal pain, rapid weight gain, nausea, vomiting, and fluid retention. Rarely, HCG injections may trigger allergic reactions, blood clots, or vision changes.
The likelihood of side effects can be reduced by following the doctor’s prescribed dosage, timing, and monitoring protocols. Immediate medical attention is required if severe symptoms such as intense abdominal pain, swelling of legs, or difficulty breathing occur after the injection.
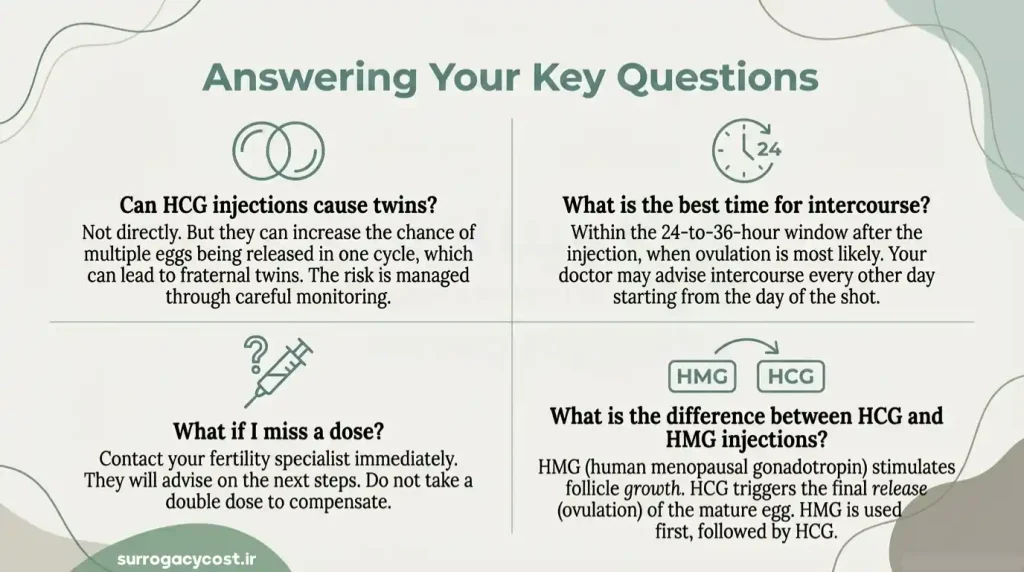
HCG injections themselves do not directly cause twins, but they can increase the chances of multiple ovulations, which may lead to fraternal twins or higher-order multiples. When HCG is used to trigger ovulation, it can sometimes stimulate more than one egg to mature and release in the same cycle.
Women undergoing fertility treatments like ovulation induction or IVF are more likely to conceive twins if multiple eggs are released and fertilized. The risk of multiples depends on factors such as age, ovarian reserve, and the response to fertility medications, rather than the HCG injection alone.
While HCG can indirectly raise the possibility of twins, careful monitoring by a fertility specialist helps manage and predict the likelihood of multiple pregnancies.
The best time to have sex after an HCG injection is typically 24 to 36 hours post-injection, as this is when ovulation is most likely to occur. Timing intercourse within this window increases the chances of sperm meeting the egg for fertilization.
Some fertility specialists recommend having sex every other day starting the day of the injection and continuing for a few days to ensure that sperm are present when ovulation happens. Using ultrasound monitoring or ovulation tests can help confirm the exact timing of ovulation, making conception more likely.
Following the doctor’s guidance for timing intercourse is crucial, as too early or too late can reduce the chances of successful fertilization, even if ovulation occurs.
The best time to have sex after an HCG injection is typically 24 to 36 hours post-injection, as this is when ovulation is most likely to occur. Timing intercourse within this window increases the chances of sperm meeting the egg for fertilization.
Some fertility specialists recommend having sex every other day starting the day of the injection and continuing for a few days to ensure that sperm are present when ovulation happens. Using ultrasound monitoring or ovulation tests can help confirm the exact timing of ovulation, making conception more likely.
Following the doctor’s guidance for timing intercourse is crucial, as too early or too late can reduce the chances of successful fertilization, even if ovulation occurs.
Missing a dose of HCG can affect the timing of ovulation and reduce the chances of successful conception. The impact depends on how far along the treatment cycle you are and the purpose of the injection. If the injection was meant to trigger ovulation, delaying it can result in eggs not maturing properly or ovulating at the wrong time.
It is important to contact your fertility specialist immediately if a dose is missed. They may reschedule the injection or adjust the timing of ovulation monitoring to minimize disruption. Patients should never self-administer a double dose to compensate, as this can increase the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) and other side effects.

HCG injections can sometimes cause false positive results on pregnancy tests. Since these injections introduce HCG into the body, home urine tests or blood tests may detect the hormone even before fertilization occurs, leading to a misleading positive result.
This effect is most common when a pregnancy test is taken too soon after an HCG injection, usually within 7–14 days, before the injected HCG has cleared from the body. The concentration of HCG from the injection can remain in the bloodstream and urine, triggering a test result that mimics early pregnancy.
To avoid confusion, doctors typically recommend waiting at least 10–14 days after ovulation or HCG injection before taking a pregnancy test. Blood tests performed at a fertility clinic can also differentiate between injected HCG and HCG produced by a developing pregnancy, providing more accurate results.
HCG injections play a key role in fertility treatments by triggering ovulation and supporting early hormonal changes necessary for conception. When used correctly, they can significantly increase the chances of pregnancy, especially in women undergoing ovulation induction or IVF cycles.
The success rate depends on factors such as age, ovarian reserve, overall reproductive health, and timing of intercourse or embryo transfer. Women with normal ovarian function who respond well to HCG injections generally have higher chances of conceiving, while those with conditions like PCOS or low ovarian reserve may experience lower success rates.
Combining HCG injections with careful monitoring of follicle development, luteal phase support, and proper timing of insemination or embryo transfer helps maximize pregnancy outcomes. Fertility specialists tailor HCG use to each patient’s needs to improve the likelihood of successful conception.

Even after an HCG injection, pregnancy may not occur due to several factors. One common reason is timing issues, where ovulation does not align with intercourse or insemination. Poor egg quality or low ovarian reserve can also prevent fertilization, even if ovulation occurs successfully.
Hormonal imbalances, such as low progesterone or thyroid problems, may hinder implantation of a fertilized egg. Structural issues like blocked fallopian tubes or uterine abnormalities can also prevent pregnancy. Additionally, male factor infertility, including low sperm count or motility, can reduce the chances of conception despite proper ovulation.
Sometimes, the body may not respond adequately to the HCG injection, meaning ovulation does not occur as expected. Close monitoring by a fertility specialist is essential to identify these factors and adjust treatment for better outcomes.
Early signs may include implantation spotting, mild cramping, breast tenderness, fatigue, and nausea, appearing about 1–2 weeks after ovulation. Hormonal changes from HCG can also cause subtle mood swings or increased sensitivity.
Ovulation usually occurs 24 to 36 hours after the HCG injection, depending on the individual’s response and follicle maturity. Proper timing is crucial for conception during this fertile window.
HCG injections can sometimes lead to ovarian cyst formation, particularly if multiple follicles are stimulated or the ovaries over-respond. These cysts are usually temporary but should be monitored by a doctor.
Two HCG injections may be administered when follicles mature at different rates or to improve ovulation chances in women who respond slowly. This approach ensures at least one mature egg is released.
HCG injections trigger ovulation, whereas HMG (human menopausal gonadotropin) stimulates follicle growth and maturation before ovulation. Often, HMG is used first, followed by HCG to induce egg release.
Yes, taking a pregnancy test too soon after an HCG injection can result in a false positive, because the injected hormone may still be present in blood or urine. Waiting 10–14 days is recommended for accurate results.
Yes, men may receive HCG injections to boost testosterone levels and stimulate sperm production, particularly in cases of low testosterone or certain fertility issues.
For accurate results, it’s recommended to wait at least 10–14 days after the HCG injection, allowing the hormone from the injection to clear and any natural HCG from pregnancy to be detected.
Typically, one correctly timed HCG injection is sufficient to trigger ovulation. Additional doses are only given under medical supervision if ovulation does not occur as expected.
No, HCG injections are not required during a normal pregnancy, as the placenta produces adequate HCG naturally. Unnecessary injections may cause hormonal imbalance or other side effects.
If HCG is administered after ovulation, it does not trigger another egg release and may have minimal effect on the cycle. Its benefits are mostly limited to pre-ovulation timing.
An HCG 5000 injection is sometimes used in fertility treatments to support the luteal phase and maintain progesterone production, ensuring the uterine lining remains ready for implantation and early embryo development.
HCG injections are a critical tool in fertility treatments, helping to trigger ovulation, support the luteal phase, and improve the chances of conception. Understanding how HCG works, the proper timing, dosage, and administration methods is essential for achieving successful outcomes while minimizing risks.
While HCG can increase the likelihood of pregnancy, it is not a guaranteed solution and may sometimes lead to side effects like ovarian cysts, false-positive pregnancy tests, or, in rare cases, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Careful monitoring by a fertility specialist ensures that injections are given safely and at the right time for optimal results.
Women and men considering HCG injections should follow medical guidance closely, as individual factors like age, ovarian reserve, hormonal balance, and underlying health conditions significantly affect treatment success. With proper supervision, HCG injections can be a powerful aid in overcoming fertility challenges and achieving a healthy pregnancy.
